In Control and Coordination chapter we should learn about the process / function by which plants and living being perform their daily activities.
General definition in Control and Coordination
Stimuli: The response and reaction given by the living organism due to change in environment are called stimuli. for example foul smell of trash due to which you cover your nose. The response to stimuli by living organism is takes place which the help of their sense organs like nose, eyes, ears etc.
Response: The response of stimuli given by living organism is usually in form of some movements of their body part.
Coordination: The working together of various organ of an organism in systematic manner so that we can produce proper response to stimulus is called coordination.
Control and Coordination in plant
Plant do not have nervous system and sense organ like the animal but they can still sense things. The plant coordinate their behavior against environment changes by using Hormones.
Plant Hormones (Phytohormones)
The control and coordination in plant is done by plant hormones. Plant hormones coordinate the activities of plant by controlling one or other aspects of growth of plant so plant hormone are also known as plant growth substance.
There are four major types of plant hormones which involve in control and coordination in plants. These are Auxin, Gibberellins, Cytokinins and Abscisic Acid.
- Auxin: Auxin are plant hormones which promotes cell enlargement, cell differentiation in plants. It promotes food growth. It is made by cells at the tip of stems and roots. Auxin move away from light and toward gravity. Auxin has opposite effect on growth of stem and roots. Auxin speed up growth in stems but slow down growth in roots.
- Gibberellins: This hormone promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation in presence of Auxin. Gibberellins helps in breaking of dormancy in seeds and buds. It also promote growth in fruits.
- Cytokinin: This plant hormone promote cell division in plants, help in breaking of dormancy of seed and buds. They delay the ageing in leaves. It promote opening of stomata and also food growth.
- Abscisic Acid: It promote dormancy of seed and bud. It promote closing of stomata, falling of leaves (Abscission). It also cause the detachment of flowers and fruits from plant.
Tropic Movement (Tropism)
A growth movement of plant part in response to external stimulus in which direction of stimulus determine direction of response is called Tropism. There are two type of Tropism that are Positive Tropism and Negative Tropism.
Positive Tropism: The growth of plant parts is move toward the stimulus is called positive tropism.
Negative Tropism: The growth of plant parts is move away from stimulus than it is called negative tropism.
Types of Tropism
- Light: Phototropism
- Gravity: Geotropism
- Chemical: Chemotropism
- Water: Hydrotropism
- Touch: Thigmotropism
Phototropism: The movement of plant part in response to light is called Phototropism. Stem bend towards light so it show Positive Phototropism. Root of plant show Negative Phototropism.
Geotropism: The plant’s part response after influencing of gravity is called Geotropism. If plant part move in direction of gravity it is called Positive Geotropism. on the other hand if plant part move against the direction of gravity than it is called Negative Geotropism.
Chemotropism: The movement of plant part in response to chemical stimulus is called Chemotropism. Such as pollen tube grow toward the sugar substance secreted by the ripe stigma of carpel in flower.
Hydrotropism: The movement in response to water by plant’s part is called hydrotropism. If the plant part move toward water it is called Positive Hydrotropism while if plant part move away from water than it is called Negative Hydrotropism.
Thigmotropism: The direction of growth movement of plant part in response to touch of an object is called Thigmotropism. The climbing part of plant such as tendril grow toward any support which they happen to touch and wind they support so tendril of plant are Positive Thigmotropism.
Nastic Movement
The movement of plant part in response to an external stimulus in which the direction of response is not determined by the direction of stimulus is called Nastic Movement. The nastic movement of plant are induce by stimuli such as heat, light, touch. The main difference between Trophic and Nastic Movement is that Trophic Movement is directional movement of plant part but Nastic Movement is not a directional movement of plant with respect to the stimulus. For example opening up of the petal of dandelion flower in morning in bright light and closing in evening when light fade, The closing of petal of moon flower in morning in bright light and opening at dark when light fades.
Thigmonasty
The non directional movement of plant part in response to touch of an object is called Thigmonasty. For example The sensitive plant has pad like structure called pulvini at base of each leaf. The pulvini contain lot of water in their cell due to internal water pressure in them. All Pulvini are firm and hold the leaves above them upright. The folding up of leaves of sensitive plant on touching is due to the sudden loss of water from pulvini. So, it loose their firmness causing the leaves to drop and fall.
Photonasty
The non directional movement of plant part in response to light is called photonasty.
Coordination in Animal
Endocrine System: The control and coordination in higher animal called Vertebrate takes place through Nervous System as well as Hormonal System called Endocrine System.
Nervous System: System made up of nerves cell is called Nervous System.
Receptor
A receptor is a cell or group of cell in sense organ which is sensitive to particular type of stimulus such as light, sound, smell, taste, heat, pressure etc.
Types of Receptors
- Photoreceptors: Detect light (present in eyes)
- Phonoreceptors: Present in inner ears
- Olfactory Indicator: Detect smell (present in nose)
- Gustatory receptors: Detect taste (present in tongue)
- Thermal Receptor: Detect heat or cold (present in skin)
- Hydrotropism Receptor: Movement due to water
So there are two system of coordination of activity in human those are Nervous System and Endocrine System.
Human Nervous System
The human nervous system receive information from the surrounding process they interpretate it and respond accordingly. The unit which make up the nervous system are called nerves cell or neuron. So, neuron is the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Neuron
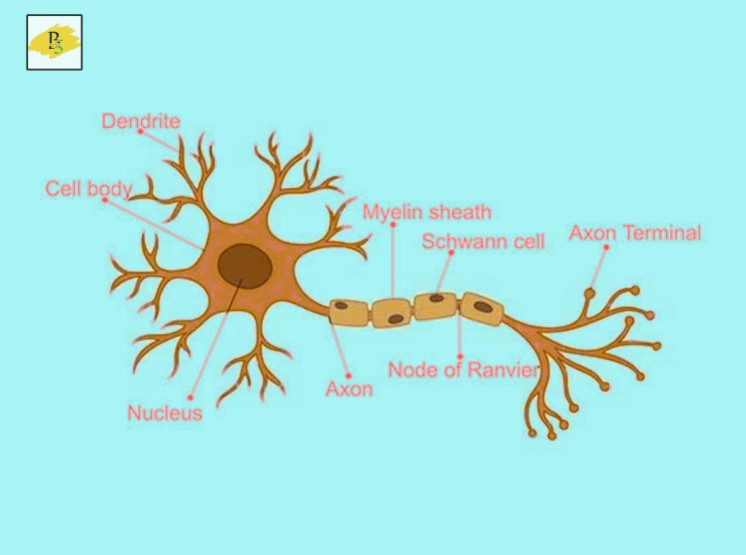
Neuron has three components i.e. Cell body, Dendrite and Axon
- Cell Body: It consist of cytoplasm and a nucleus. A number of long and thin fiber are stretching out from the cell body of neuron. They are called Nerve Fibers.
- Dendrites: The shorter fibers on the body of neuron are called dendrites. The dendrites pick up the nerves impulse from receptor.
- Axon: The longest fiber on the cell body of neuron called axon. The Axon has an insulating and protective sheath of myelin around it (Myelin is made of fat and protein). The junction between two adjacent neuron in which the electric impulse pass is called Synapse.
Types of Neuron
Neuron are of three types
- Sensory Neuron: These neuron transmit impulses from sensory cells toward the Central Nervous System (Spinal Cord and Brain).
- Motor Neuron: These neuron transmit impulses from Central Nervous System toward the muscle cells.
- Relay Neuron: These occur in Central Nervous System where they act as link between other neurons.
Synapse: A microscopic gap between a pair of adjacent neurons over which nerve impulses pass when going form one neuron to the next is called a Synapse.
Organs of Human Nervous System
The main organ of Nervous System are brain, spinal cord and nerves different sense organ helps in functioning of nervous system.
Parts of Nervous System
- Central Nervous System: CNS consist of Brain and Spinal Cord.
- Peripheral Nervous System: PNS consist of all the nerves of the body like cranial nerves, spinal nerves and visceral nerves. It can be further divided into two parts Voluntary Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System.
Peripheral Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous system consists of all the nerves of the body, their are mainly three types of nerves which form peripheral nervous system.
- Spinal Nerves: They arise from spinal cord along most of the length of spinal nerves are spread throughout the body except the head. They all carry both sensory and motor neuron and are described as mixed neuron.
- Cranial Nerves: These are from the brain and spread throughout the head.
- Visceral Nerves: These are special kind of nerve which mostly arise from spinal cord. They are connected to the internal organs of the body.
Reflex Action: The quick and simplest response given by nervous system comes under reflex action. It is a rapid automatic response to a stimulus which is not under the voluntary control of the brain. For ex sneezing, coughing, blinking of eyes etc.
Reflex Arc: The path way taken by nerve impulses during reflex action is called reflex arc.
Note: The reflexes which involve only spinal cord are called spinal reflexes. Those reflex action which involve brain are called cerebral reflexes.
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System means self growing nervous system. It is a specific network of nerves in the body which control the process like breathing, heart beat, digestion, sweating etc. This systems controls and regulates the function of internal organ of our body involuntarily (on it own).
Voluntary Nervous System
The action which need thinking and which are performed by us knowingly are called voluntary action. For ex writing a letter, dancing, cycling etc.
Central Nervous System
It consist of the brain and the spinal cord. The work of Central Nervous System is to direct incoming messages to the motor neurons that are connected to the part of the body which will respond to a stimulus.
Brain
It is the highest coordination center in the body. It is located inside the skull of our body. It is protected by a bony box inside the skull called cranium. The brain is surrounded by three membranes called Meninges, which help to protect it. The space between the membrane is filled with a cerebro spinal fluid which protects the brain from mechanical shocks.
The brain is divided into three parts that are fore brain, mid brain and hind brain.
- Fore Brain: It consist mainly cerebrum. It is the site of an learning, intelligence, memory, the voluntary action of the body are coordinate by cerebrum. Cerebrum has different area for performing different actions.
- Mid Brain: Mid brain does not have any further division. It control reflex movement of head, neck and trunk in response to visual and auditory stimuli. It also control the reflex movement of eye muscle, change in pupil size and the shape of eye lens.
- Hind Brain: Hind brain consist of pons, cerebellum and medulla oblongata. Cerebellum help in maintaining posture and balance of the body. It also coordinate smooth body movement, such as walking, moving, dancing, cycling etc.
Medulla control various involuntary action such as Heartbeat, breathing, controlling center for reflexes (coughing, vomiting, sneezing etc.), blood pressure etc.
Spinal Cord
It is cylindrical in structure. It begins in continuation with medulla and extend downward. It is enclose in bony cage called vertebral column. It is also surrounded by meninges. Their are 31 pairs of nerves arise from spinal cord.
Function of Brain
The brain receive information carrying nerve impulse from all sensory organ of body. The brain respond to the impulses brought in by sensory organs by sending its own instruction to the muscles. Brain corelate the different stimuli from different sense organ. Brain sends information so that behavior can be modified according to the past experience.
Hormones
These are the chemical substance which coordinate the activities of living organism and also their growth.
Characteristics of Hormones
- These are secreted in small amount.
- These are poured directly in to the blood and carried through out the body by blood circulation.
- Hormones act on the target organs.
- Hormones coordinate the activities of body.
Glands
A gland which secrete its product in body. A Gland is made up of group of cells or tissues. There are two types of gland in the body i.e. Exocrine gland and Endocrine gland.
Exocrine gland: These gland have duct that secrete enzymes.
Endocrine gland: These are ductless gland and secrete hormones.
Note: Some glands in our body secrete both exocrine and endocrine function. These are Pancreas, Testes, Ovary etc.
Read More: Simplified notes of The human eye and the colourful world.






